By 200 BC, China used simple wind machines to pump water, while in Persia and the Middle East, vertical-axis windmills with sails woven from reeds were already used to grind grain.
What is wind energy? The force of the wind
Since the beginning of time, people have used the wind to benefit and perform actions that are not possible with their strength.
This resource has allowed people to use windmills to grind wheat, pump water from wells, and even deploy sails to sail the sea. Today, windmills are one of the leading renewable energy sources for generating electricity.
Technological evolution and innovation have contributed decisively to the development of wind energy, up to modern wind turbines. According to the National Electric Coordinator (CEN*), as of May 2024, there are over 5,000 MW of installed wind farms in Chile, achieving participation of over 14% of the total generation capacity of the National Electric System.
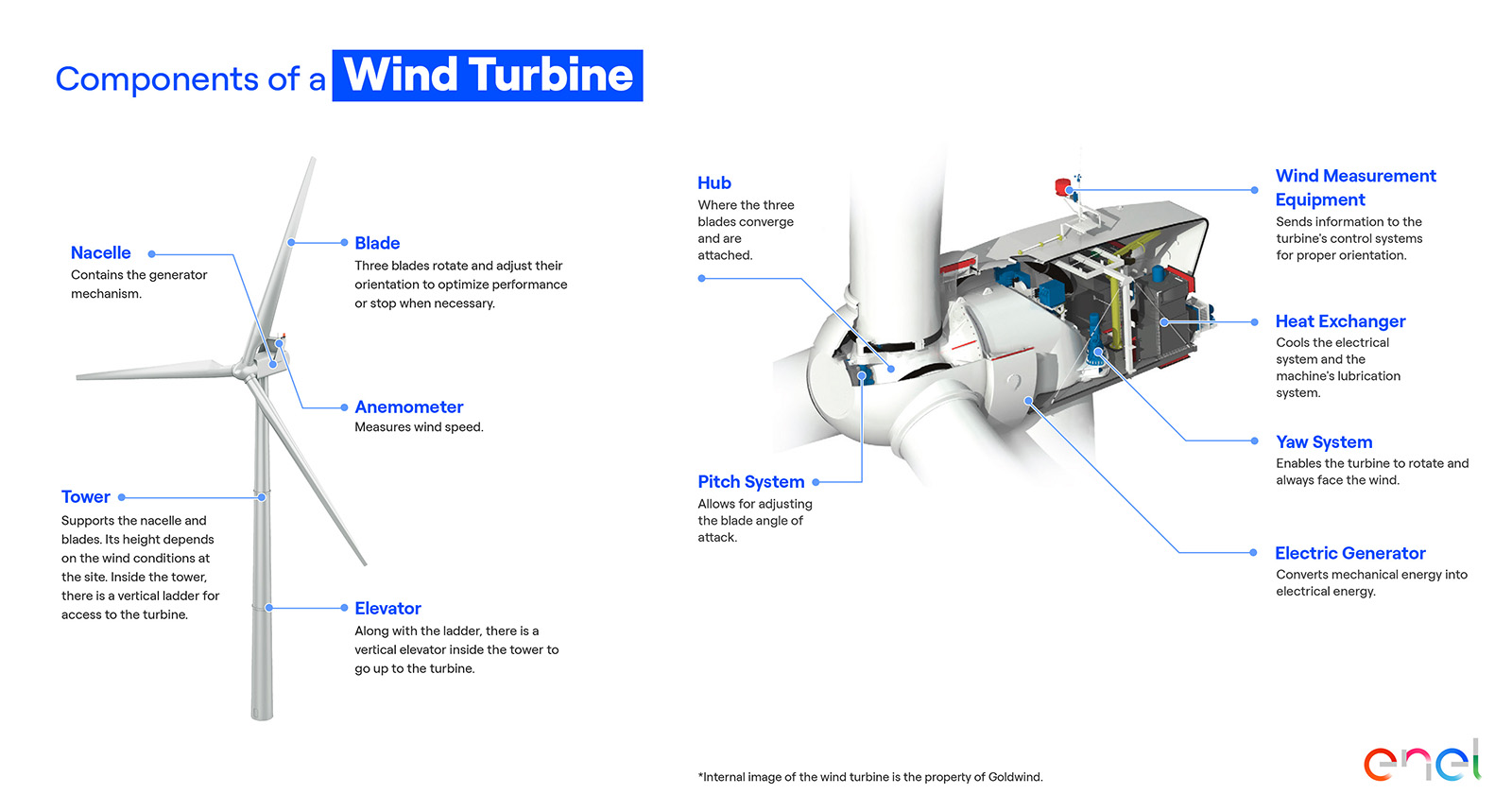
What does a wind turbine look like, and how does it work?
Wind turbines are composed of a tower, a nacelle, and blades that capture wind energy and transform it into electrical energy.
In order to generate this type of energy, the wind spins blades that are designed to capture the maximum kinetic energy of the wind. This energy is then converted into mechanical energy by the rotor located in the nacelle. Subsequently, the mechanical energy is transferred to an electric generator, which is transformed into electricity.
Once produced, cables transport electrical energy to a transformer, which collects the electricity generated by the various wind turbines in the wind farm, raises its voltage, and makes it available to the grid.