The history of solar energy began in 1883 with Charles Fritts's creation of the first solar cell. Using a sample of semiconductor selenium coated with a thin layer of gold, Fritts demonstrated that it was possible to generate electricity from sunlight. Although this initial device had an efficiency of less than 1%, his innovation laid the foundation for the development of solar technology.
What is Solar Energy? An Inexhaustible Source of Energy
Solar energy is an inexhaustible source of energy that plays a crucial role in life on Earth. It drives vital processes such as photosynthesis in plants, which in turn sustains the food chain but also drives natural phenomena such as winds, tides, and fossil fuels. The Sun is, in essence, the engine of almost all forms of energy on our planet.
With the advent of technological progress in the late 19th century, it became possible to transform solar energy into electricity using solar cells. These devices convert solar radiation into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect.
As of July 2024, Chile had 9,880.19 MW of solar generation, achieving a penetration of 29.02% in the energy system. Enel Chile contributed 2,050 MW of such generation.
How does solar energy work?
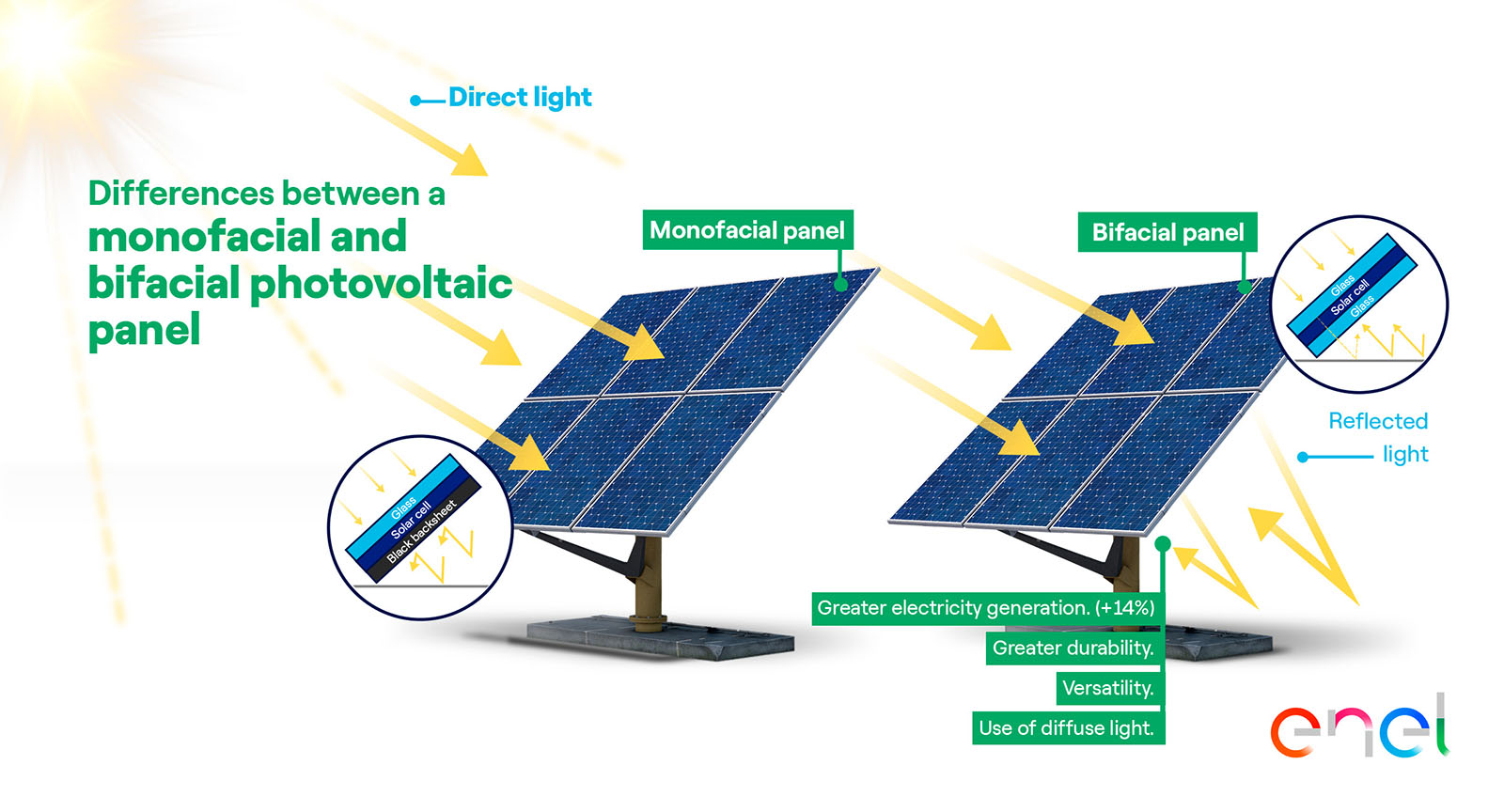
The key to this energy is solar panels. These panels are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon, which generate electricity when exposed to sunlight, thanks to the photovoltaic effect. The panels are mounted on structures that ensure optimal tilt and orientation to maximize sunlight collection.
Each photovoltaic panel in a solar farm is connected to a machine called an inverter, which converts the direct current generated by the panel modules into alternating current, facilitating the transport of energy and its use in homes thanks to a control system that manages the operation of the farm and connects the electricity produced to the grid, making it available for consumption.