Hydroelectric Energy in the National Electric System
According to the National Electric Coordinator (CEN), as of May 2024, the installed capacity of hydroelectric plants in the National Electric System is around 7,500 MW, representing approximately 21% of the country’s total installed capacity. According to the Ministry of Energy's basin study, Chile has a Hydroelectric Energy potential of around 16,000 MW.
Types of hydroelectric plants in Chile
Enel operates two types of Hydroelectric Energy plants in Chile, adapted to the country’s geographical and climatic characteristics. These are:
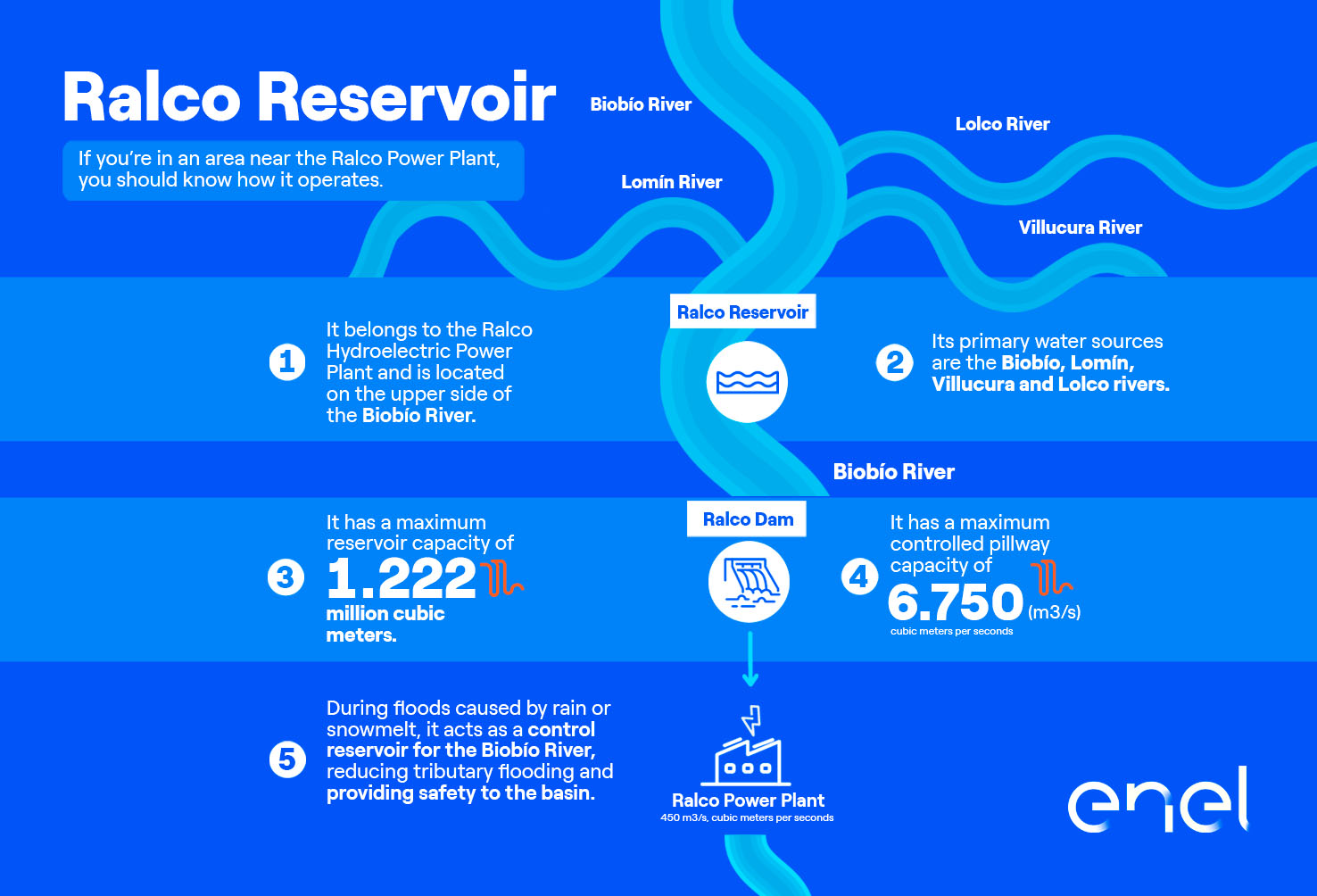
- Reservoir Plants: These plants store large volumes of water in reservoirs, allowing for flow regulation and ensuring production in line with the national electric system and market needs. These plants include Rapel, Cipreses, Pehuenche, El Toro, Ralco, and Pangue.
- Run-of-River Plants: These plants take advantage of the continuous flow of rivers without incorporating large reservoirs, generating electricity steadily with minimal impact on the natural environment. These plants include Los Molles, Sauzal, Sauzalito, Isla, Ojos de Agua, Curillinque, Loma Alta, Abanico, Antuco, Palmucho, Pullinque, and Pilmaiquén.
Innovation and efficiency at Enel
At Enel, we operate hydroelectric plants with advanced technologies that allow us to maximize water's energy potential. These plants achieve exceptional performance and contribute significantly to the generation of clean energy in Chile.
Our hydroelectric plants are an integral part of our strategy to lead the energy transition toward a more sustainable future. They generate renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions.


